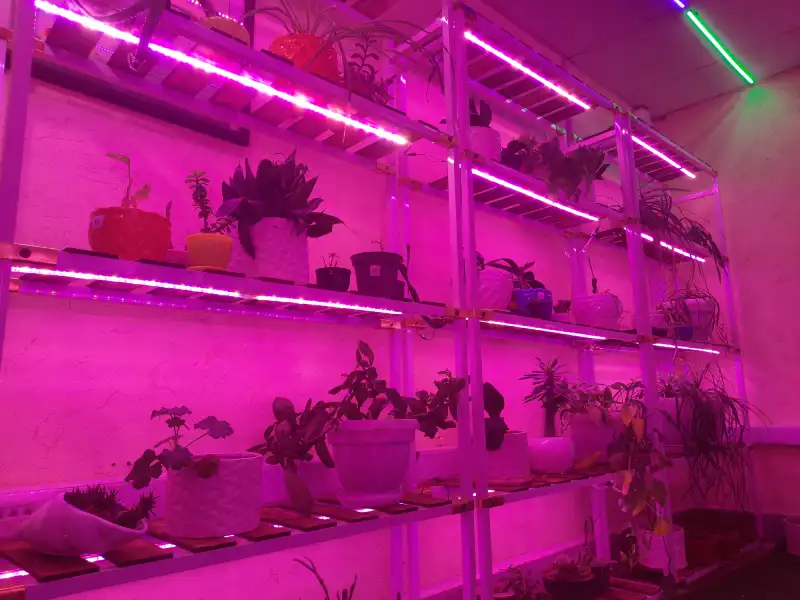
Plant grow lights have revolutionized indoor gardening, enabling enthusiasts and professionals alike to cultivate thriving plants year round, regardless of natural sunlight availability. Whether you're growing herbs in your kitchen, nurturing exotic flowers, or managing a commercial hydroponic setup, understanding plant grow lights is essential for success.
Plant grow lights are artificial light sources designed to mimic the sun’s spectrum, providing the specific wavelengths of light plants need for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, fueling growth, flowering, and fruit production. Unlike regular household lights, grow lights emit light in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) spectrums, which are critical for vegetative growth and flowering, respectively.
These lights are used in various settings, including:
Indoor gardening:
For houseplants, herbs, or vegetables in homes or apartments.
Greenhouses:
To supplement natural light during cloudy days or short winter months.
Hydroponics and aquaponics:
For soil-less growing systems that rely entirely on artificial lighting.
Commercial farming:
To maximize crop yields in controlled environments.
By providing consistent light, grow lights allow gardeners to control plant growth cycles, improve yields, and cultivate plants in spaces with little to no natural sunlight.
Why Use Plant Grow Lights?
Natural sunlight isn’t always available or sufficient, especially in urban environments, northern climates, or during winter. Plant grow lights offer several advantages:
1. Year-Round Gardening:
Grow lights enable you to cultivate plants regardless of season or weather.
2. Controlled Environment:
Adjust light intensity, duration, and spectrum to optimize plant growth stages.
3. Space Efficiency:
Grow plants in small apartments, basements, or vertical farming setups.
4. Enhanced Yields:
Proper lighting can boost flowering, fruiting, and overall plant health.
5. Energy Efficiency:
Modern LED grow lights consume less power compared to traditional lighting systems.
Whether you're a hobbyist or a commercial grower, grow lights provide the flexibility to create ideal growing conditions.
Types of Plant Grow Lights
Choosing the right grow light depends on your plants’ needs, budget, and growing setup. Here are the most common types of plant grow lights:
1. LED Grow Lights
Overview:
Light Emitting Diode (LED) grow lights are the most popular choice due to their efficiency and versatility.
Pros:
Energy-efficient, consuming up to 50% less power than other lights.
Long lifespan (up to 50,000 hours).
Customizable spectrums for specific growth stages.
Low heat output, reducing the risk of plant burn.
Cons:
Higher upfront cost.
Quality varies; low-cost LEDs may lack full-spectrum capabilities.
Best For:
All types of plants, from seedlings to mature crops, in both home and commercial setups.
2. Fluorescent Grow Lights
Overview:
Fluorescent lights, including Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs) and T5 tubes, are affordable and widely available.
Pros:
Low cost and easy to find.
Good for small-scale setups or beginners.
Produce less heat than HID lights.
Cons:
Less energy-efficient than LEDs.
Limited light intensity, less suitable for large plants or fruiting crops.
Best For:
Seedlings, clones, or low-light plants like herbs and leafy greens.
3. High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Grow Lights
Overview:
HID lights, including Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS), are powerful and traditional options.
Pros:
High light output, ideal for large-scale or commercial grows.
Effective for flowering and fruiting stages (HPS).
Proven track record in professional horticulture.
Cons:
High energy consumption.
Generate significant heat, requiring cooling systems.
Shorter lifespan than LEDs.
Best For:
Large plants, flowering crops, or professional greenhouse operations.
4. Plasma and Induction Grow Lights
Overview:
These are newer, less common technologies offering full-spectrum light.
Pros:
High efficiency and long lifespan.
Broad spectrum similar to natural sunlight.
Cons:
Expensive and less widely available.
Limited use in mainstream gardening.
Best For:
Advanced growers experimenting with cutting-edge technology.